Supply and demand curve in drawing a demand curve we assume that
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
If you’re studying economics, or just interested in understanding how the market works, you’ve likely heard of the supply and demand curve. These two lines represent the forces that interact to set prices for goods and services. But how exactly do you draw a supply and demand curve?
When it comes to drawing a supply and demand curve, many people find themselves struggling with where to start or how to properly plot the data. Some may also wonder what factors influence the shapes of these curves.
To draw a supply and demand curve effectively, you need to have a basic understanding of the law of supply and demand. This law asserts that, all other things being equal, the price and quantity of a good or service will move in opposite directions.
In summary, to draw a supply and demand curve, you need to first plot the data for price and quantity demanded or supplied on a graph. Then you need to connect the points to form a line for each curve.
My Personal Experience Drawing a Supply and Demand Curve
When I first encountered the concept of supply and demand curves in my economics class, I found it confusing and difficult to understand. However, once I started drawing them on a graph, it became clear how they interacted and why they moved in different directions. Now, I find it fascinating to study how these curves shift in response to changes in the market.
Understanding the Factors That Influence the Shape of Supply and Demand Curves
The shape of a supply or demand curve is influenced by several factors. The elasticity of demand and supply determines how much the quantity demanded or supplied will change in response to changes in price. Beyond this, the availability of substitute goods, the size of the market, the cost of production, and external factors like weather or legislation can all impact the shape of the curve.
The Importance of Market Equilibrium
One crucial aspect of understanding how to draw a supply and demand curve is understanding the concept of market equilibrium. Market equilibrium is the point where the quantity supplied is equal to the quantity demanded, resulting in an ideal price for both buyers and sellers. Understanding how to locate market equilibrium is key to analyzing the factors that impact supply and demand.
Key Takeaways for Drawing a Supply and Demand Curve
When it comes to drawing a supply and demand curve, keep in mind the following key takeaways:
- The law of supply and demand states that price and quantity move in opposite directions
- To draw a curve, plot the data and connect the points
- The shape of the curve is influenced by elasticity, availability of substitutes, production costs, and other factors
- Market equilibrium is the point where the quantity supplied is equal to the quantity demanded
Applying Concepts of Supply and Demand to Real-World Examples
Understanding how to draw a supply and demand curve can help you understand why prices fluctuate for goods or services. For example, if there is a sudden shortage of avocados due to extreme weather conditions, then the demand for them will exceed supply, resulting in a higher price. By studying market trends and observing the supply and demand curves, you can gain insight into how the economy works and why certain goods or services may be priced the way they are.
Question and Answer
Q: What is the difference between the law of supply and the law of demand?
A: The law of supply states that, all other things being equal, as the price of a good or service increases, the quantity supplied will increase. The law of demand states that, all other things being equal, as the price of a good or service increases, the quantity demanded will decrease.
Q: What determines whether a good or service is inelastic or elastic?
A: The elasticity of demand or supply for a good or service refers to how responsive buyers or sellers are to changes in price. If demand or supply is inelastic, then small changes in price will not greatly affect the quantity demanded or supplied. If demand or supply is elastic, then small changes in price will greatly affect the quantity demanded or supplied.
Q: Can the supply curve ever be vertical?
A: Yes, the supply curve can be vertical if the quantity supplied is fixed regardless of the price. This is seen in cases where the cost of production becomes too high, such as with natural resources that are depleting.
Q: How can I use the concept of market equilibrium to make informed economic decisions?
A: By understanding the concept of market equilibrium, you can identify when a good or service is overpriced or underpriced, and make decisions accordingly. For example, if you notice that the current price of a good is much higher than the equilibrium price, you may decide to hold off on purchasing it until the price drops back down.
Conclusion of How to Draw a Supply and Demand Curve
Knowing how to draw a supply and demand curve is a fundamental skill that can help you better understand how the market works. By mastering this concept, you can gain insight into why prices fluctuate for certain goods and services, and make informed decisions based on market trends.
Gallery
Supply Curve | Definition, Graph, & Facts | Britannica

Photo Credit by: bing.com / demand daya alam penawaran permintaan kalkulasi britannica investing nepal neoliberal
Demand (AS/A Levels/IB/IAL) – The Tutor Academy
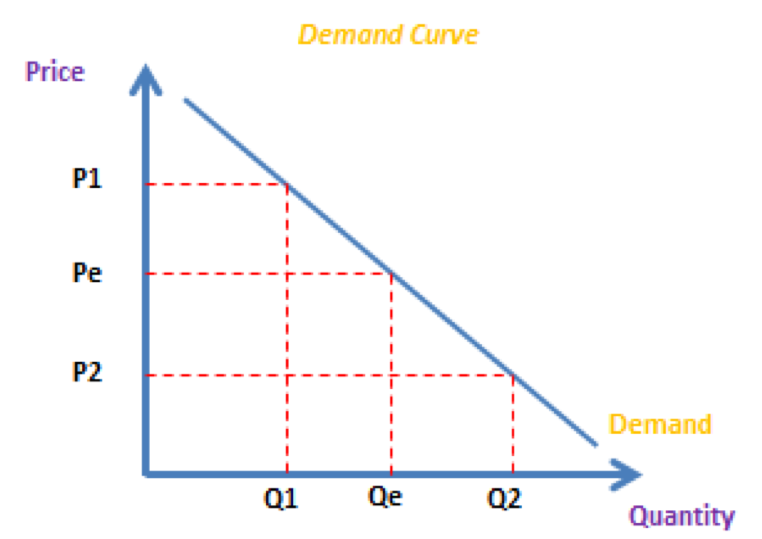
Photo Credit by: bing.com / demand curve graph supply draw ial increase price ib levels exam marks lose incorrect labeling accurately diagrams tip does
Supply And Demand Curve / In Drawing A Demand Curve We Assume That
Photo Credit by: bing.com /
Supply And Demand Curves Diagram Showing Equilibrium Point Stock
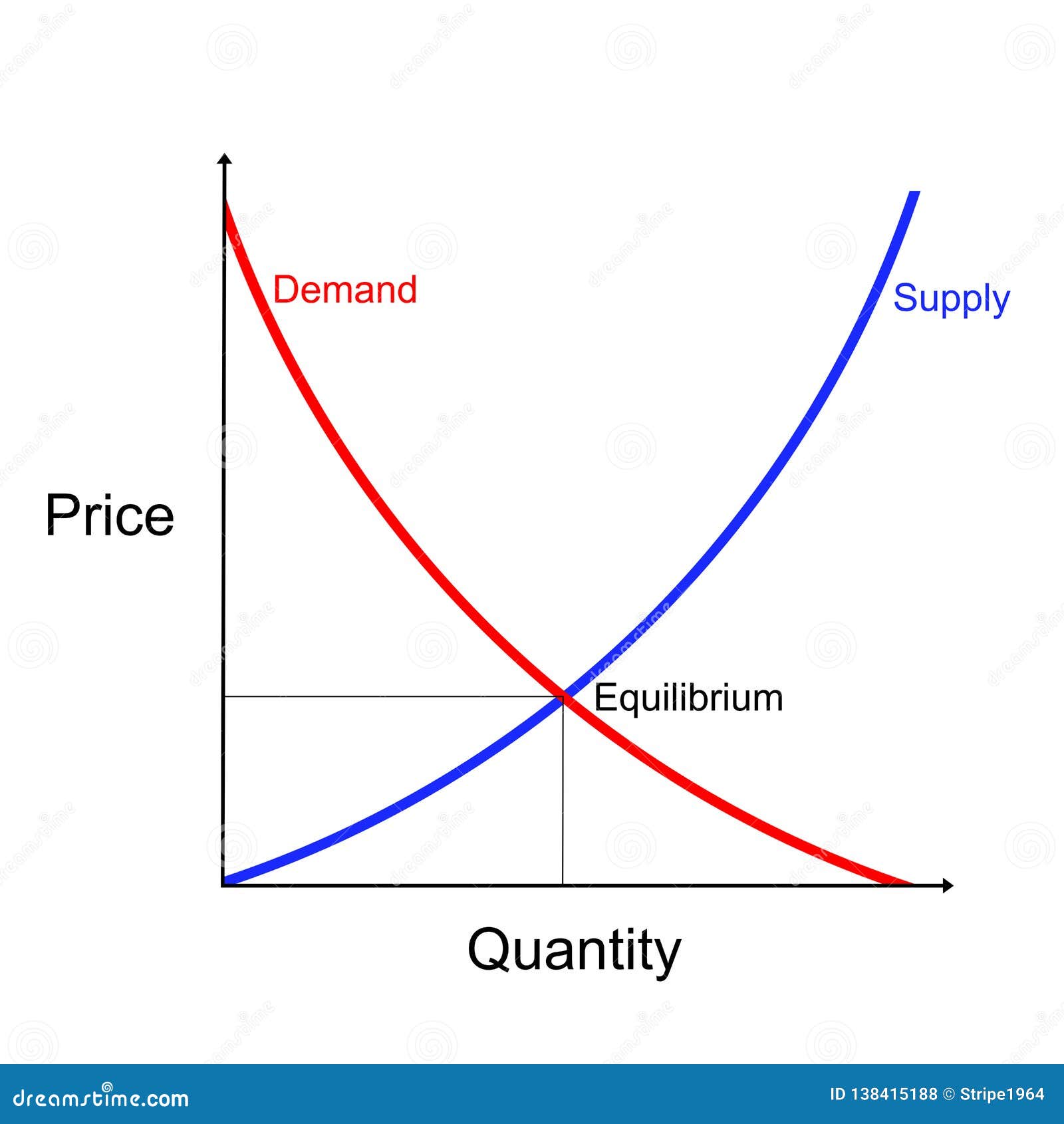
Photo Credit by: bing.com / equilibrium curves graph
Supply And Demand Curve : Perfect Competition II: Supply And Demand
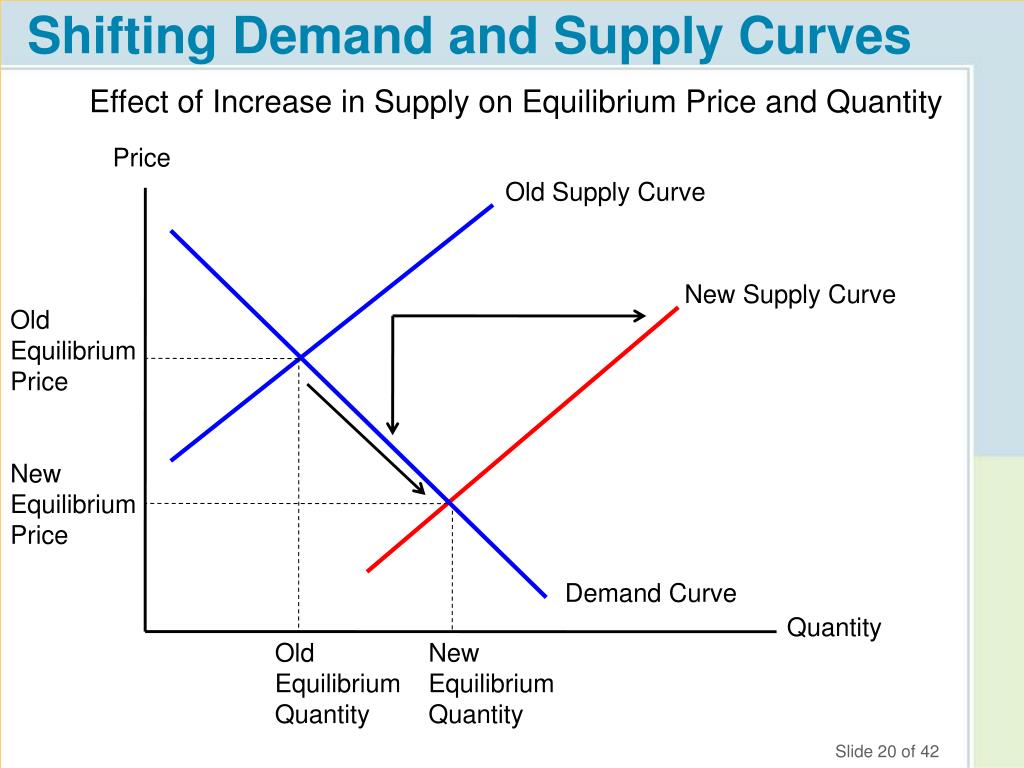
Photo Credit by: bing.com / supply curves equilibrium economics shifting