Steam turbine
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Are you struggling with how to draw velocity diagrams for turbines? Do you find it confusing and overwhelming? Well, fear not, as this article will guide you step by step on how to draw velocity diagrams for turbines in a simple and easy-to-understand way.
When it comes to drawing velocity diagrams for turbines, there are many technical terms and concepts that can be challenging to understand. Additionally, the process may seem complicated and time-consuming, leading to frustration and confusion.
The velocity diagram for turbines represents the velocity angles and magnitudes of fluid as it passes through a turbine. It is an essential tool used to evaluate the performance of a turbine and optimize its design.
Now, let’s break down the steps to draw a velocity diagram for turbines:
Step 1: Identify the Inlet and Outlet Velocity
The first step is to identify the fluid velocity at the inlet and outlet of the turbine. These values are usually provided in the problem statement or can be calculated using fundamental principles of fluid mechanics.

Step 2: Draw the Inlet and Outlet Lines
Next, draw a line to represent the inlet and outlet velocity on the diagram. Connect the two lines to form a triangle. This triangle is known as the velocity triangle for the turbine.
Step 3: Draw the Blade Velocity Triangle
Draw a line perpendicular to the inlet and outlet lines, representing the blade velocity of the turbine. This line should pass through the midpoint of the inlet and outlet lines.

Step 4: Determine the Blade Angle and Deviation Angle
Using the blade velocity triangle, determine the blade angle and deviation angle. The blade angle is the angle between the blade velocity and the inlet velocity, while the deviation angle is the angle between the outlet velocity and blade velocity.
Step 5: Analyze the Results
Finally, use the calculated blade and deviation angles to assess the performance of the turbine. These values can be manipulated to optimize the design and improve the turbine’s efficiency and power output.
Common Mistakes when Drawing Velocity Diagram for Turbines
One common mistake made when drawing velocity diagrams for turbines is incorrectly identifying the inlet and outlet velocities. It is essential to verify these values before proceeding with the diagram to ensure accuracy.
Another mistake is forgetting to account for the blade velocity, which can significantly impact the results and accuracy of the diagram.
Personal Experience with Drawing Velocity Diagram for Turbines
As a mechanical engineer, I have had my fair share of experience drawing velocity diagrams for turbines. However, it was not until I began working on a real-world project that I fully appreciated the importance of this tool.
The velocity diagram provided critical insights into the performance of the turbine, which allowed us to optimize the design and significantly improve its efficiency and power output.
Benefits of Drawing Velocity Diagram for Turbines
The primary benefit of drawing velocity diagrams for turbines is the ability to evaluate and optimize the performance of the turbine. By identifying areas of inefficiency or weakness, engineers can make the necessary adjustments to improve its operation and output.
Additionally, velocity diagrams can be used to compare different turbine designs and assess their relative performance and efficiency, helping to inform decision-making processes and optimize design choices.
FAQs about Drawing Velocity Diagram for Turbines
Q: What are the benefits of drawing a velocity diagram for turbines?
A: The primary benefit of drawing a velocity diagram for turbines is the ability to evaluate and optimize the performance of the turbine. Additionally, velocity diagrams can be used to compare different turbine designs and assess their relative performance and efficiency.
Q: What is a blade velocity triangle for turbines?
A: A blade velocity triangle for turbines is a diagram that represents the blade velocity angle, inlet velocity, and outlet velocity of fluid as it passes through a turbine.
Q: How do I determine the blade angle and deviation angle for a velocity diagram?
A: Use the blade velocity triangle to calculate the blade angle and deviation angle. The blade angle is the angle between the blade velocity and the inlet velocity, while the deviation angle is the angle between the outlet velocity and blade velocity.
Q: What common mistakes should I avoid when drawing a velocity diagram for turbines?
A: The most common mistakes when drawing velocity diagrams for turbines are incorrectly identifying the inlet and outlet velocities and forgetting to account for the blade velocity.
Conclusion of How to Draw Velocity Diagram for Turbines
In summary, drawing a velocity diagram for turbines is a crucial tool for assessing and optimizing turbine performance. By following the steps outlined in this article and avoiding common mistakes, engineers can improve the efficiency and output of turbines for a wide range of applications.
Gallery
Steam Turbine | Velocity Triangle Of Steam Turbine | MechanicalTutorial

Photo Credit by: bing.com / velocity steam inlet triangle portion represents
Velocity Diagram Of Impulse Turbine | Lecture 1 (Part 2) - YouTube

Photo Credit by: bing.com / velocity turbine impulse diagram
Types Of Steam Turbine - A Basic Overview - ShipFever

Photo Credit by: bing.com / turbine axial velocity triangle flow steam types stage gas direction blades turbomachinery principle reaction working spin ignited does triangles diagram
Pelton Wheel - Parts, Working, Diagram, Applications , Advantages

Photo Credit by: bing.com / pelton turbine
ロイヤリティフリー V T Graph For Uniform Acceleration - 我がメガと
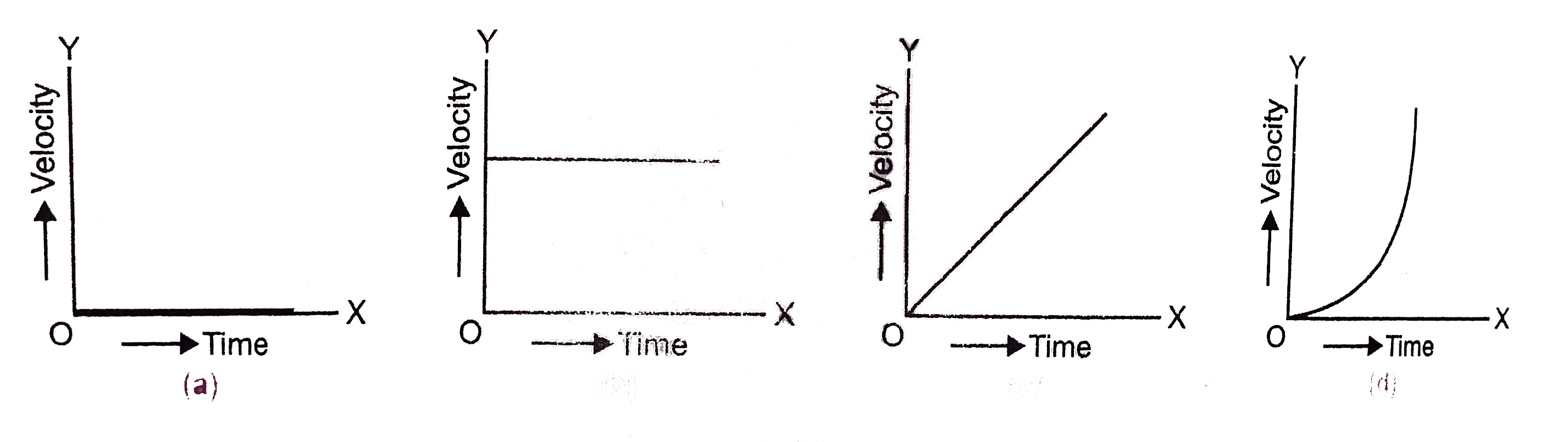
Photo Credit by: bing.com /